How do you communicate company policies to your employees? The thumb rule for any organization is to share information on company policies with all employees immediately after onboarding. But how do you share it effectively? How do you monitor if they read it or not? There may be many ways to share, like an email or memo, PDFs, word documents, etc. But are they effective in today’s world?
📝 TL;DR: One-Minute Brief
- An employee handbook outlines company policies, expectations, benefits, and values, serving as a vital HR resource.
- It improves onboarding, legal compliance, workplace culture, and internal transparency.
- Key Components: Includes company values, comprehensive employment details, compensation, employee conduct, safety policies, training, and development.
- Steps to build: define objectives, conduct research, know what policies to avoid, identify core focus areas, review and revise, and make regular updates and maintenance.
- Stress-free Employee Handbook Tips: Keep it engaging, gather employee feedback, present your handbook carefully, and focus on the language and tone.
- Tools like Document360 help manage, version, and present handbooks accessibly.
Many organizations have started investing more in building more structured and easily accessible employee handbooks.
What Is An Employee Handbook?
An employee handbook is a detailed document that contains the company’s policies, procedures, expectations, vision, and mission. It acts as a virtual HR, showing the employees both their internal rights and their obligations within the company.
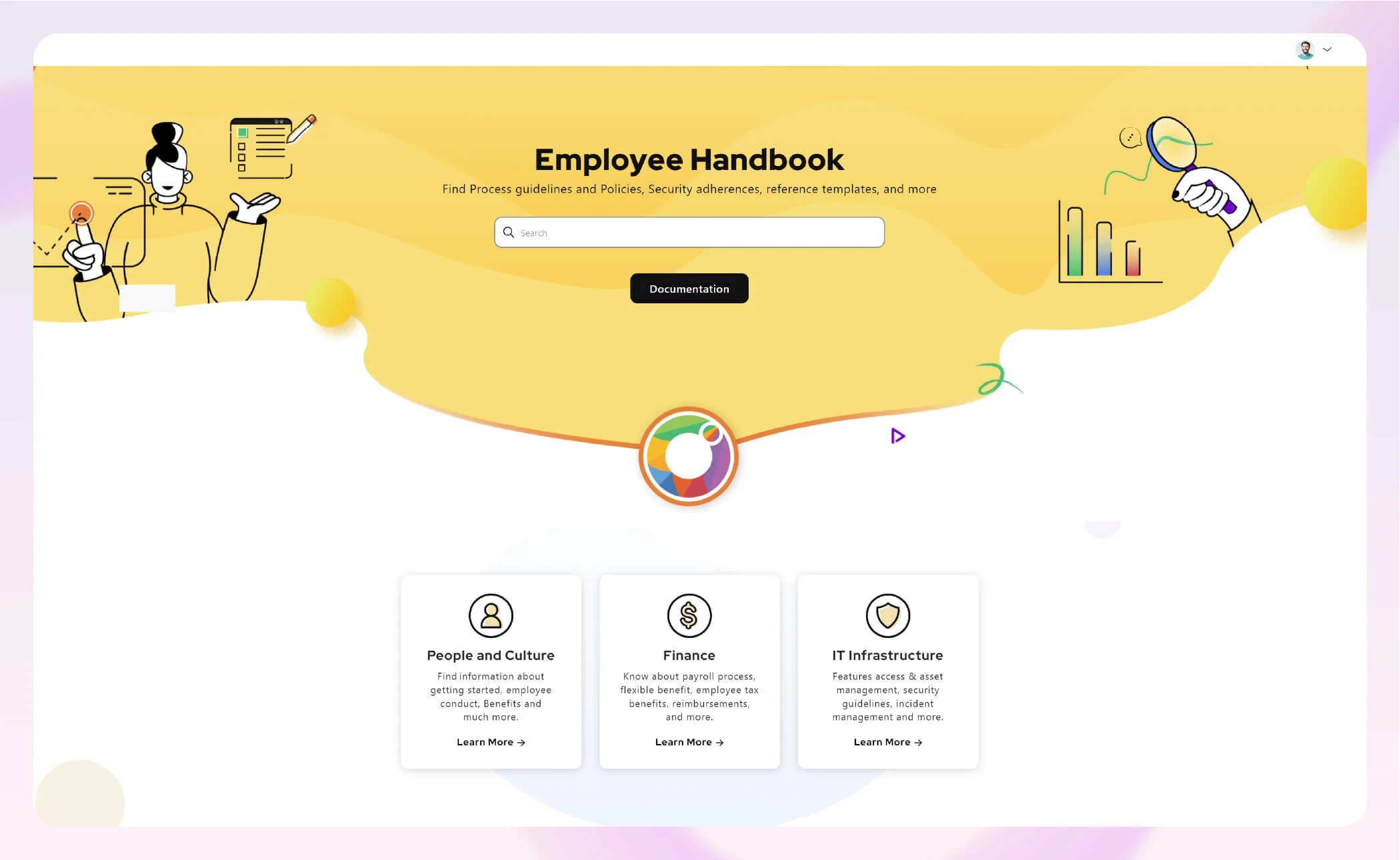
Example of Employee handbook created in Document360 for our Parent company, Kovai.co.
Employee handbooks should be given to employees during the onboarding process so they can become familiar with company policies at the very beginning of their employment period. It can be provided electronically or in hard copy, and all employees will be required to indicate that they have read it.
Why Is It Important?
As said earlier, an employee handbook is not something to do as an afterthought. It is of much importance for several reasons (apart from diversity).
First, it offers the simplicity and uniformity of communicating the company policies, procedures, and expectations to employees.
For example, All employees have the right to paid holidays, say 21 days of holidays in a year. The information is how many days are available, how working hours are calculated, and what the procedure is to apply for leave. Everything is documented in the employee handbook.
Besides, the handbook complies with the law by providing details regarding the existing laws and regulations governing employment. In instances where employees need instructions on how discrimination or harassment policies are put in place to equate with an employee-friendly workplace.
The handbook is also a directory for employees seeking information about benefits, compensation, and performance expectations. When an employee would like to know if they are entitled to a vacation, the manual enunciates the clear regulations.
Finally, the handbook makes a fair playing field possible in the sense that both employers and workers are aware of exactly what they can expect from each other. If the workers fully know their rights and responsibilities, it will promote a good work culture and less tension or fights.
Key Components of Employee Handbooks
Now, what makes a good employee handbook in the first place? Here’s what you should look for:
Company Values and Mission Overview
Just as the saying goes that a man without a vision has no future, the same goes for businesses.
The first key component of an employee handbook is the company values and mission overview.
Note: Creating a distinct and unique set of principles for a business is not accomplished by referring to a template.
A company needs to select values that resonate with its mission, vision, and culture. If it doesn’t, what makes the employee handbook yours? These would become the bedrock of any decision-making–the model for shaping companies’ cultures and the voice that results in communication with customers, employees, and shareholders.
A 2011 study showed that companies with well-aligned cultures and innovations have 30% higher enterprise value growth and 17% higher profit growth than companies with low degrees of alignment.
Employees who relate to the company’s values and mission together are found to be more involved and more focused on the future and success of the business.
Comprehensive Employment Details
This component contains information that an employee needs about working at the company. It includes:
- Recruitment and hiring procedures
- Employee classifications and job roles – what jobs are workers doing in the organization, and what tasks connect to each job’s responsibilities?
- Compensation and benefits packages: In short, it allows employees to know their income, medical insurance, or retirement plans.
- Performance evaluation processes – state assessment standards and the manner of employees’ supervision and assessment.
- Policies regarding leave – information concerning all the holidays, such as weekends, staff holidays, sick leave, and other employee benefits
- Disciplinary procedures and grievance mechanisms
- Termination guidelines and procedures
- Commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion
- Legal requirements related to employment
- Resources for employees
Compensation and Benefits
This section talks about salary, bonuses, perks – everything!
- Salary Structure: Base salary, bonuses, and other financial incentives – their breakdown to the employees.
- Performance-based Bonuses: What are the standards for doling out bonuses, and what conditions do employees need to satisfy to earn them?
- Equity Options: Do employees have stock options or equity cast in their remuneration plan?
- Profit-sharing Plans: Does the company have an equity-sharing policy and if so, does it detail how this process takes place?
- Health Insurance: What insurance plan options are available to employees, and what do they cover?
- Retirement Plans: Are employer-sponsored options available?
- Paid Time Off: What type of paid leave do employees get? Is the company generous in providing vacation, sick leave, holidays, and time off for special occasions?
- Professional Development Opportunities: How is the organization going to encourage its employees to pursue more challenging positions and improve their skills, like via on-the-job training, tuition reimbursement, or mentorship programs?
Good to note: Factors such as salary and benefits must be designed equitably, with clear expectations for the labor market and satisfied workers, to bring in top professionals and keep the workforce happy. You know what they say, “Happy employee = Happy customer = Successful company.”
Employee Conduct and Discipline
This is about employees’ professionalism, ethics, and policy adherence. Here is a breakdown of what it covers:
- The code of conduct
- Anti-discrimination and harassment policies
- Intellectual property protection:
- Social media usage guidelines
- Confidentiality agreements
- Conflict resolution procedures
Things to know: A guideline with a penalty structure for violation helps to build an atmosphere of safety and respect, and it also suppresses conflicts in the workplace.
Safety and Security
When writing provisions relating to safety, reference should be made to applicable laws such as the Federal Occupational Safety and Health Act. The information covered in this section is as follows:
- Workplace Safety Protocols: Including protocols for ergonomics, fire safety, accident reporting, hazard identification, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Emergency Evacuation Procedures: Evacuation routes, assembly points, and communication protocols during emergencies such as fires, natural disasters, or security threats.
- Confidentiality Agreements: Agreements outlining the company’s expectations regarding the handling and safeguarding of confidential information, trade secrets, and proprietary data.
- Data Protection and Privacy Policies: Shows how the organization maintains records and provides for the security of the data while strictly complying with data protection and privacy laws, such as secure data transmissions and disposal, data policies for handling data breaches, and other security incidents.
- Acceptable Use of Company Equipment and Resources: Outline of rules that enables everyone to understand the expected etiquette and responsibilities associated with their work equipment, computer systems, tools, and software among others. It also covers information with regards to unauthorized access, downloading of malicious codes, and proper security for password management!
The procedures of dealing with these give the whole company a culture that strengthens trust, responsibility, and accountability, where the employees become accountable for themselves and others.
Technology and Equipment Usage
This section is the go-to guide for navigating technology, using the company’s software, and the equipment employees can use.
It lays down these principles of accountability and legality – what’s allowed and what’s not, along with software licensing agreements, data, and any restrictions on personal use of infrastructure owned by the business or its network. It runs from the very basics to the most important ones.
Besides, setting policies for the technology and data use is more than just a compliance matter. It also helps increase the productivity, and security of company assets and protect the company from data breaches and misuse of resources in the industry.
Training and Development
Keeping an eye on the latest trends and technologies is a must. This section is like having an employee training and development goldmine within your organization.
It promotes your company’s commitment to continuous learning and professional growth; evident from the onboarding documentation processes, training programs, workshops, conferences, mentorship opportunities, tuition reimbursements, and career development initiatives!
According to LinkedIn, 94% of employees will stay at a company longer if it invests in their careers.
Disclaimer
A suitable disclaimer contains three main clauses:
- An employer makes it clear that the handbook isn’t a contractual agreement.
- The company isn’t subject to legal liability.
- It emphasizes the company’s ability to update/alter its policies without prior notice,
Hence, helps to manage employee expectations regarding policies in the handbook. Therefore, it makes sense to place a disclaimer at the start – or better yet, at the end – in a popularized and understandable format.
Build smart, searchable employee handbooks with Document360 today!
GET STARTED
How To Create The Best Employee Handbook For Your Small Business?
A poorly written handbook is arguably worse than having no handbook at all since it can only lead to problems that result in unnecessary expense for the company and undermine employee morale.
Let’s see what it takes to make the best handbook for employees.
1. Define Objectives and Scope
To start, you need to define the goals and scope.
Is there any sense in having a manual if you can’t ensure it describes what it’s supposed to do and what it covers?
To make the guide more useful and effective for all employees, it is vital to define specific objectives and scope that will familiarize everyone with the purpose, inclusion, and exclusion. To make a purposeful objective and scope:
- Indicate the primary purpose of the handbook – either to provide employees with uniformity of company policies, ensure compliance with the rules and regulations, or create a friendly working environment.
- Pinpoint the central topics, including employment policies, code of conduct, benefits, safety procedures, and disciplinary measures.
- Make the handbook specific regarding what will be covered and what won’t be.
- Align with organizational values, mission, and culture to maintain consistency across all rules and regulations.
Through definite goal setting and due coverage, the handbook can be one of the most valuable booklets for the employees, directing their activities, choices, and communications throughout the company.
2. Conduct Research on Policies
Do research on policies to make you:
- Understand the relevant local, state, and federal laws
- Provide an opportunity to anticipate and adjust to new laws and learn about current industry best practices, standards, expectations, and benchmarks for various HR policies.
- Identify potential biases or likely risk exposure for the business e.g., discrimination/harassment cases, safety problems associated with drug and alcohol abuse by employees at the workplace, etc., then make appropriate changes to create a better work environment.
- Examine what other companies in similar industries or with similar values have implemented so you can get ideas on how to apply them in your organization.
Good to note: You can get information from professional forums, legal sources, research papers, academic journals, and government agencies, among others.
Remember to critically evaluate the credibility and authority of your sources. Cross-referencing information from different reliable sources can help ensure that what you are looking at regarding the research is accurate and complete.
3. Know What Policies To Avoid
Someone must look for legal advice to remain updated on employment laws and policies to make the handbook compliant and adaptable towards promoting a healthy working environment.
Do not use laws that are illegal, excessively limited, as well as ambiguous. Avoid cliches and challenging language when structuring them to be understandable for every employee.
Also note that the contribution of these policies may vary depending on the demands, regulations, and norms of each SaaS company.
4. Draft Policies and Procedures
Start by identifying the core focus areas, such as code of conduct, communication guidelines, attendance policies, remote work policies, data security, intellectual property, and regulatory codes that apply to your industry.
This is how you draft a policy:
- Define why the policy is being written
- Consider using a template when writing the policy–you don’t have to start from scratch
- Prepare for policy application
- Get feedback and assign enforcers
- Put the policy into practice and improve on It
Including company policies and procedures in your employee handbook may differ depending on factors like the size of your organization and the nature of work. Comply with state and federal labor laws, including those under the Family Medical Leave Act (FMLA), Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA), amongst others.
5. Review and Revise
Once the draft process of policies and procedures is finished, continually review and revise the employee handbook.
Seek comments, locate legal and policy updates, examine the handbook for clarity and readability, maintain consistency, execute a legal assessment, focus on new subjects or policies for legal review, inform employees about the changes, and schedule the ongoing review process.
6. Regular Updates and Maintenance
Creating the best employee handbook is not a one-time project.
You need a system for regular updates and maintenance to keep the handbook accurate, relevant, and compliant year after year. Also, maintain a version control system for changes and updates to the employee handbook.
One approach to maintaining a version control system in the handbook is to assign a new number to each revised policy. Another approach is to ensure that your employee handbook, in the table of contents, includes the dates of each policy update.
Whichever method you select, it is important to maintain an audit trail of an employee’s acknowledgment of the most updated version currently in effect.
Encourage employees to provide feedback on the handbook and its policies; you can do this via a survey or suggestion box. Consider regular check-ins with employees for their feedback to ensure that you are considering all employment scenarios and how each policy change might impact their daily work.
Conduct regular training sessions or workshops to ensure employees are well-informed about the policies and procedures outlined in the handbook, and communicate any revisions or updates to these policies. Employees might forget a policy exists if they are not reminded frequently.
Tips To Manage Your Employee Handbook Stress-Free
Your employee handbook would become a piece of cake to write with just four simple tricks.
- Keep it light and engaging: Now, consider this scenario where the firm is drafting the code of conduct. Instead of writing down rules, you may use emoji to depict particular behaviors. For instance, the handheld emoji “🤝” could signify “Respect your colleagues,” and the light bulb emoji “💡” could mean “Encourage creativity and innovation”, like this, the rules become more interesting.
- Gather feedback from employees: After employees receive the handbook, organize an informal feedback session during a team meeting. Prompt everyone to mention one thing they liked about the book and one thing they think needs improvement.
- Think about the presentation of your handbook: Imagine a segment on workplace safety. Use big letters to draw attention to more important pieces and also highlight with colors like “SAFETY FIRST!”, or use bold to emphasize the major safety regulations such as “Always wear your PPE⛑️🦺🧤“. The italic type can be used to stress additional rules like “Emergency exits should be unobstructed”.
- Focus on the language and tone you’re using: Use common everyday words that everyone can relate to. Instead of legal jargon, make policy explanations explicit, like ‘‘Be respectful to coworkers’’ instead of ‘‘Maintain professional decorum in interpersonal interactions.’’.
Takeaway
Crafting a comprehensive employee handbook is necessary for creating a good working environment, complying with the law, and increasing employee participation. Employees who have handbooks are more efficient and better prepared to meet unforeseen events. Moreover, it allows workers to concentrate on more useful tasks while enhancing your company’s functionality.




 –
– 

